Creating a Sustainable Tropical Farm: Embracing Self-Sufficiency and Minimizing Store-Bought Products
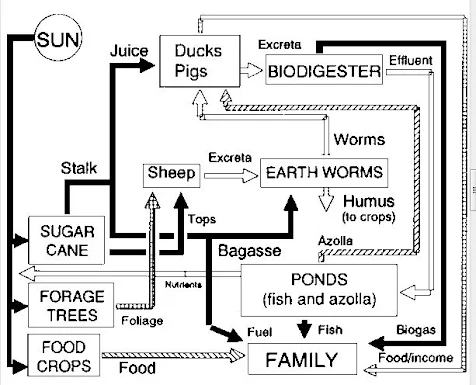
In today’s world, where environmental concerns and self-sufficiency are gaining increasing importance, creating a sustainable farm that relies on minimal outside inputs is a noble endeavor. By embracing self-sufficiency and reducing our dependence on external resources, we can minimize our ecological footprint but also foster a more resilient and economically viable farming system. In this blog post, we will explore practical steps and strategies to help you establish a sustainable farm that relies on self-sufficiency and minimizes the use of store-bought products.
Before embarking on your journey towards a self-sufficient farm, it is crucial to assess your farm’s needs and resources. Conduct a thorough analysis of your land, climate, soil quality, and available resources such as water sources and existing infrastructure. This assessment will help you determine the most suitable crops, livestock, and farming practices for your farm. It may be necessary to build needed infrastructure onto the land.
ECHO recommends figuring out what the locals are growing and eating, and then grow that. Another method might be to research what grows well in other geographical areas that have similar climates, and try to grow those things too. For example, Florida has a climate similar to New South Wales, so many of the plants that grow well there will probably grow well in Florida, such as Kangkong.
One of the key aspects of a sustainable farm is maintaining healthy soil. Instead of relying on store-bought chemical fertilizers, embrace organic composting methods to enrich your soil naturally. Composting kitchen scraps, animal manure, and plant waste can provide nutrient-rich compost that improves soil fertility and structure. Additionally, consider implementing perennial agriculture and cover cropping techniques to further enhance soil health and reduce the need for external inputs.
To reduce reliance on store-bought seeds, learn the art of seed saving and propagation. Save seeds from your best-performing plants, ensuring they are open-pollinated varieties. By doing so, you can preserve the genetic diversity of your crops and adapt them to your specific growing conditions over time. Additionally, explore the practice of plant propagation through cuttings, grafting, and division to expand your plant stock without purchasing new plants.
Pests can pose a significant challenge to any farm, but chemical pesticides should be avoided due to their high cost and negative impact on the environment and beneficial organisms. Implement integrated pest management (IPM) techniques to control pests effectively. Encourage natural predators, such as birds, lizards, and beneficial insects, to thrive on your farm. Use physical barriers, companion planting, and crop rotation to deter pests. Regularly monitor your plants for signs of pest infestation and take prompt action to prevent the spread of pests.
Integrating livestock into your farm can enhance its sustainability and self-sufficiency. Animals can provide valuable resources such as manure for composting, natural pest control, and even food. Consider raising chickens or ducks for eggs and meat, goats for milk and weed control, or bees for pollination and honey production. Properly managed livestock can contribute to a closed-loop system, where waste from one aspect of the farm becomes a resource for another.
To further reduce reliance on outside inputs, explore renewable energy options for your farm. Install solar panels or wind turbines to generate electricity, reducing your dependence on the grid. Additionally, implement water conservation techniques such as rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and water-efficient practices to minimize water usage and reliance on municipal water supplies.
Creating a sustainable farm that relies on minimal store-bought products is an achievable goal with careful planning and implementation. By embracing self-sufficiency, organic practices, and resource conservation, you can create a resilient and environmentally friendly farming system that not only benefits your farm but also contributes to a more sustainable future.